Teaching and Learning Resources
Bloom’s Taxonomy of Learning Objectives
Benjamin Bloom (1956) created this taxonomy as a multi-tiered model of classifying ways of thinking and learning according to six levels of complexity. It identifies three “domains” of learning; cognitive, affective, and psycho-motor, each organized as a series of levels or pre-requisites.
http://www.learningandteaching.info/learning/bloomtax.htm#ixzz1d3YDiVvA
Under Creative Commons License: Attribution Non-Commercial No Derivatives
Bloom’s Taxonomy Revised
Throughout the years, the levels have often been depicted as a stairway, leading many instructors to encourage their students to "climb to a higher (level of) thought." The lowest three levels are: knowledge, comprehension, and application. The highest three levels are: analysis, synthesis, and evaluation.
In the 1990’s a former student(s) of Bloom, Lorin Anderson revised the taxonomy and published the revision in 2001. A key change is the use of verbs rather than nouns for each of the categories and a rearrangement of the sequence within the taxonomy. The levels have often been depicted as a stairway leading many instructors to encourage their students to “climb” to higher levels of thought. This arrangement led to natural divisions of lower and higher level thinking.
Terminology changes: Note the change from Nouns to Verbs [e.g., Application to Applying] to describe the different levels of the taxonomy. Note that the top two levels are essentially exchanged from the old to the new version." (Schultz, 2005) (Evaluation moved from the top to Evaluating in the second from the top, Synthesis moved from second on top to the top as Creating.) Source:http://projects.coe.uga.edu/epltt/index.php?title=Bloom%27s_Taxonomy
Mary Forehand, University of Georgia
The revised terms are defined as:
- Remembering: Retrieving, recognizing, and recalling relevant knowledge from long-term memory.
- Understanding: Constructing meaning from oral, written, and graphic messages through interpreting, exemplifying, classifying, summarizing, inferring, comparing, and explaining.
- Applying: Carrying out or using a procedure through executing, or implementing.
- Analyzing: Breaking material into constituent parts, determining how the parts relate to one another and to an overall structure or purpose through differentiating, organizing, and attributing.
- Evaluating: Making judgments based on criteria and standards through checking and critiquing.
- Creating: Putting elements together to form a coherent or functional whole; reorganizing elements into a new pattern or structure through generating, planning, or producing.
(Anderson & Krathwohl, 2001, pp. 67-68)
ANOTHER WAY OF WORKING WITH BLOOM’S REVISED TAXONOMY
The hierarchy of the categories has been altered as well, as shown in this inverted pyramid:
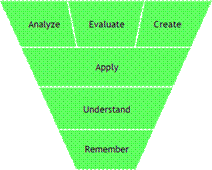
The Revised Bloom's Taxonomy (Anderson & Krathwohl, 2001, pp. 67-68)
extends into the knowledge dimension – factual knowledge, conceptual knowledge, procedural knowledge, and meta-cognitive knowledge - as well as the six processes of the cognitive dimension. A table indicating actions related to the intersection of these two domains can be useful as we seek to tap the full scope of knowledge and cognitive processes in our students. More discussion of the revised taxonomy can be found at http://oregonstate.edu/instruct/coursedev/models/id/taxonomy/#tabletaxonomy
Related Resources
http://www.learningandteaching.info/learning/bloomtax.htm

![aption: Terminology changes 'The graphic is a representation of the NEW verbage associated with the long familiar Bloom's Taxonomy. Note the change from Nouns to Verbs [e.g., Application to Applying] to describe the different levels of the taxonomy. Note that the top two levels are essentially exchanged from the Old to the New version.' (Schultz, 2005) (Evaluation moved from the top to Evaluating in the second from the top, Synthesis moved from second on top to the top as Creating.) Source: http://www.odu.edu/educ/llschult/blooms_taxonomy.htm](Academic_Integrity_clip_image002.jpg)